CSS应用示例02
等高布局
伪等高:padding+margin
.box_01 {
overflow: hidden;
font-size: 0;
}
.box_01 .equal_height {
display: inline-block;
width: 200px;
padding: 15px;
vertical-align: top;
margin-bottom: -300px;
padding-bottom: 300px;
box-sizing: border-box;
font-size: initial;
}伪等高:边框模拟
table-cell
absolute+padding
flex
grid
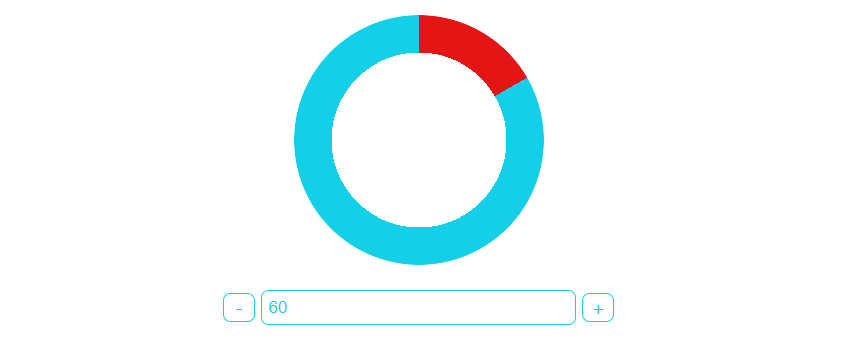
百分比环形图
最后更新于